The world of artificial intelligence (AI) is filled with complex terms and concepts, some of which can seem confusing at first glance. Two such terms are “AI Agents” and “Agentic AI.” While they might sound similar, they refer to distinct ideas within the field of AI. Understanding their differences and how they contribute to advancements in AI is crucial for anyone exploring this domain.
What Are AI Agents?
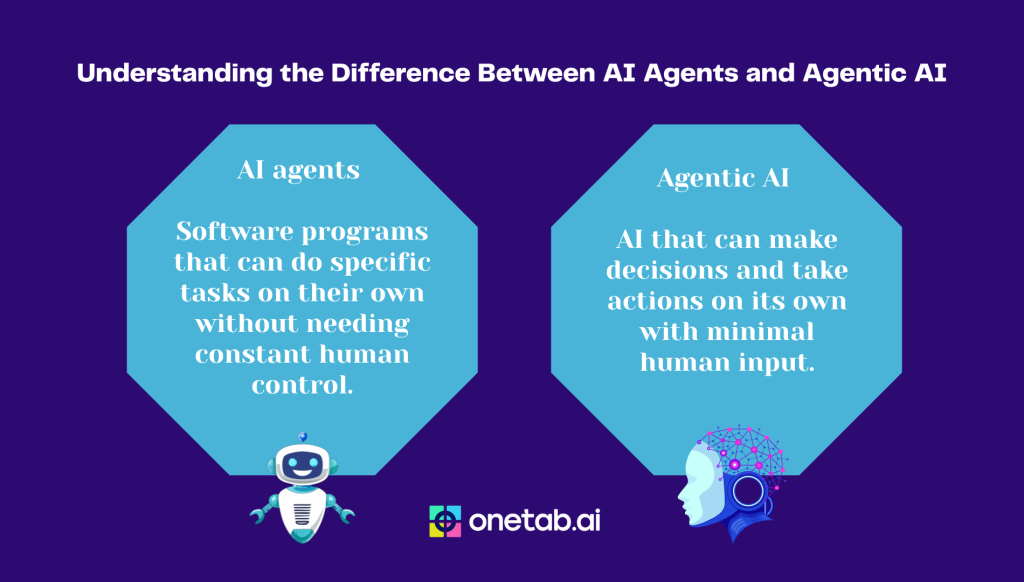
AI agents are software entities designed to perform specific tasks autonomously. They act as intermediaries between users and systems, utilizing algorithms and data to make decisions or execute actions. AI agents typically operate within defined boundaries and are programmed to achieve particular goals. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, recommendation systems on streaming platforms, and chatbots that handle customer service inquiries.
These agents rely on predefined rules, machine learning models, or a combination of both to process input, analyze data, and provide output. Their functionality is task-specific, meaning they excel in performing repetitive or specialized activities efficiently.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI, on the other hand, refers to AI systems that exhibit a higher degree of autonomy and decision-making capabilities. Unlike traditional AI agents that follow predefined instructions, agentic AI systems can perceive their environment, adapt to changes, and make decisions based on dynamic contexts. They are designed to act with a sense of purpose, pursuing long-term objectives rather than just completing isolated tasks.
Agentic AI systems often incorporate advanced technologies such as reinforcement learning, natural language understanding, and reasoning capabilities. For instance, self-driving cars can be considered an example of agentic AI because they navigate complex environments, make real-time decisions, and adapt to unpredictable scenarios.
Key Differences
1. Level of Autonomy: AI agents operate within predefined parameters, while agentic AI exhibits a higher level of independence and adaptability.
2. Scope of Functionality: AI agents focus on specific tasks, whereas agentic AI aims for broader goals that may involve multiple interconnected tasks.
3. Decision-Making: Agentic AI systems make decisions based on a deeper understanding of their environment, while traditional AI agents rely on programmed logic or limited machine learning models.
How Are They Helpful?
Both AI agents and agentic AI play critical roles in advancing the field of artificial intelligence. AI agents streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance user experiences in various industries such as healthcare, retail, and finance. They handle repetitive or time-consuming tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex responsibilities.
Agentic AI, with its advanced decision-making capabilities, is paving the way for transformative applications like autonomous vehicles, personalized education platforms, and intelligent robotics. These systems hold the potential to solve complex real-world problems by adapting to changing conditions and making informed choices.
Conclusion
While the terms “AI Agents” and “Agentic AI” may initially seem interchangeable, their distinctions lie in their scope, autonomy, and decision-making abilities. Both are valuable components of the AI ecosystem, addressing different needs and challenges. As these technologies continue to evolve, their combined potential will undoubtedly shape the future of innovation across industries. Understanding these concepts is a step toward appreciating the vast possibilities AI has to offer.