AI conversations today are full of terms like GenAI, LLMs, AI Agents, Deep Learning, NLP, and more. They’re often used interchangeably but they’re not the same thing.
If you’ve ever wondered how these buzzwords actually relate to each other, here’s a simple breakdown that connects the dots.
1️⃣ Artificial Intelligence (AI) – The Umbrella
At the top, we have Artificial Intelligence (AI).
AI is the broad field focused on building systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence – reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making.
Everything else you hear – machine learning, LLMs, GenAI – fits somewhere under this umbrella.
2️⃣ Machine Learning (ML) – Learning From Data
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI.
Instead of programming every rule manually, ML systems learn patterns from data.
Examples:
- Spam detection
- Fraud detection
- Recommendation engines
ML made AI practical and scalable.
3️⃣ Deep Learning – Powering Modern AI
Deep Learning is a subset of ML.
It uses neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to process large amounts of data. Deep learning is what enabled breakthroughs in:
- Speech recognition
- Image recognition
- Language understanding
Most modern AI systems, especially generative ones, are powered by deep learning.
4️⃣ Natural Language Processing (NLP) – Understanding Human Language
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field within AI focused on enabling machines to understand and generate human language.
Examples:
- Chatbots
- Sentiment analysis
- Translation systems
NLP relies heavily on machine learning and deep learning.
5️⃣ Large Language Models (LLMs) – The Engines Behind Modern NLP
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a deep learning model trained on massive text datasets to understand context and generate human-like responses.
Examples include:
- OpenAI’s GPT models
- Google’s Gemini
- Meta’s LLaMA
LLMs power modern chat-based systems and reasoning tools.
6️⃣ Generative AI (GenAI) – Creating New Content
Generative AI (GenAI) refers to AI systems that create new content, text, images, code, audio, or video.
LLMs are a type of GenAI focused on text.
Other examples include image generation models and code generation tools.
So:
- All LLMs are GenAI
- But not all GenAI systems are LLMs
7️⃣ AI Agents (Agentic AI) – Taking Action
If LLMs generate responses, AI Agents go one step further.
AI agents:
- Reason through tasks
- Make decisions
- Take actions using tools or APIs
- Operate autonomously toward a goal
For example:
An AI agent could:
- Read incoming emails
- Update a CRM
- Schedule meetings
- Send follow-ups automatically
Agents often use LLMs as their “brain” but add memory, planning, and tool usage layers.
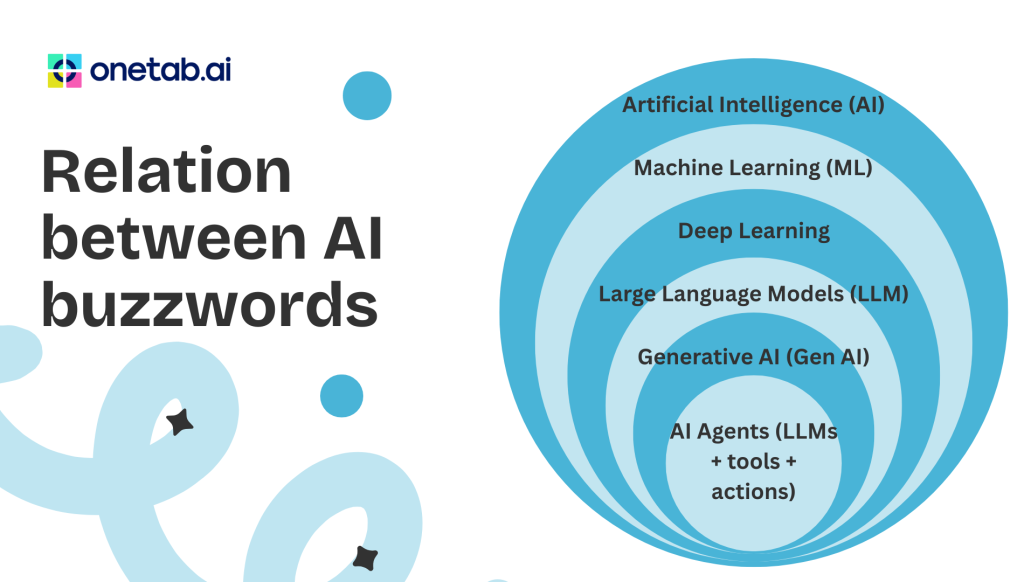
How Everything Connects (Simple Hierarchy)
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
└── Machine Learning (ML)
└── Deep Learning
└── Large Language Models (LLMs)
└── Generative AI (GenAI – text)
└── AI Agents (LLMs + tools + actions)
Think of it like this:
- AI is the field
- ML is the approach
- Deep Learning is the technique
- LLMs are specific models
- GenAI is the capability
- AI Agents are the application layer
Why This Matters
Understanding how these terms relate helps you:
- Avoid mixing up concepts
- Communicate clearly with teams and clients
- Make smarter AI adoption decisions
- Identify where real value lies
With the world moving fast in AI, clarity isn’t optional, it’s strategic.