Introduction
Productivity in software development is a multi-faceted concept, influenced by individual skills, teamwork, and the overall work environment. Measuring it can help organizations improve efficiency, but it can also be challenging to define what “productivity” truly means. There are so many variables and intangibles that come along with developing software which is why there are so many single tools and plugins dedicated to improving efficiency and productivity, yet it’s still very fragmented In this guide, we explore different methods for measuring developer productivity, discussing their advantages and limitations.
Traditional Metrics for Measuring Developer Productivity
Traditional metrics offer quantifiable ways to assess productivity but often fall short of capturing the full picture. Some common traditional metrics include:
Lines of Code (LOC): This measures the total number of lines written by a developer. While easy to quantify, it doesn’t account for code quality, complexity, or effectiveness.
Number of Commits: This tracks the frequency of code commits to a repository. Although it indicates activity, it doesn’t necessarily reflect meaningful contributions.
Completed Tasks/Features: This focuses on the number of tasks or features completed within a given timeframe. It can help measure output but might encourage shallow solutions over deeper problem-solving.
These traditional (and somewhat outdated) metrics are often criticized for encouraging quantity over quality, potentially leading to lower code quality and increased technical debt.
This is why concepts like the SPACE framework were created..
The SPACE Framework of Developer Productivity
The SPACE Framework of Developer Productivity is a holistic approach to thinking about and measuring software developer productivity. The SPACE framework is not a list of metrics or benchmarks. Instead, it outlines five different dimensions of productivity that can inform your own definition of productivity, and by extension, your measurements.
The five SPACE framework dimensions are
1. Satisfaction and Well-being: How satisfied developers are with their work and working conditions, and how healthy and happy they are.
2. Performance: How well the software fulfills its intended purpose, both from a quality perspective, but also in terms of user impact.
3. Activity: A count of the actions within a system, such as number of tests, builds, and design documents produced by a team of developers.
4. Communication and Collaboration: How well your team members communicate with each other and work together.
Efficiency and Flow: The ability of your team to complete work with minimal interruptions and make continuous progress.
Not only does SPACE emphasize the importance of all five categories, it goes further to explain that both workflow metrics as well as perception metrics, like how productive a developer feels, are equally as important when defining and measuring developer productivity.
Beyond Traditional Metrics: Holistic Approaches
So to better capture the essence of developer productivity, consider broader, more holistic approaches:
1. Code Quality and Maintainability: Tools can measure code quality, focusing on factors such as complexity, code smells, and maintainability. This approach emphasizes the importance of writing clean, maintainable code.
2. Impact and Outcomes: This measures the real-world impact of code changes, focusing on the value delivered to end users or business objectives. It shifts the focus from “how much” to “how effective.”
3. Collaboration and Communication: Developer productivity often relies on teamwork. Tools like Onetab or GitLab provide insights into collaboration patterns, helping to identify areas for improvement.
4. Time to Value: This measures how quickly a team can deliver valuable features or products. It can be a good indicator of productivity while promoting customer-centric development.
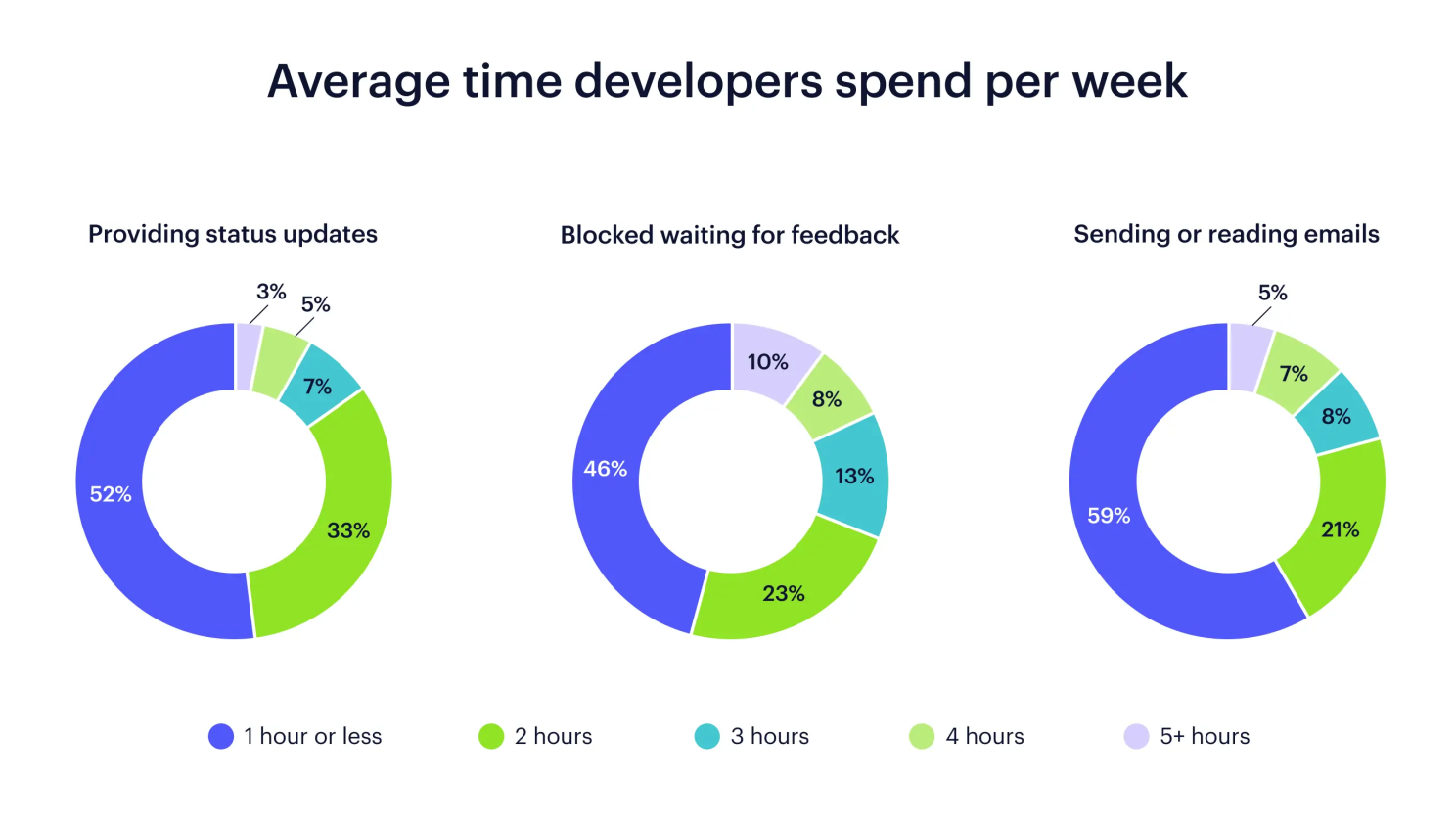
Best Practices for Measuring Developer Productivity
To measure developer productivity effectively, consider these best practices:
1. Define Clear Objectives: Establish what productivity means for your organization. Are you focused on speed, quality, customer satisfaction, or innovation?
2. Use a Combination of Metrics: A single metric may not capture the full spectrum of productivity. Consider combining multiple metrics to gain a holistic view.
3. Prioritize Quality and Sustainability: Encourage developers to focus on creating maintainable code that delivers long-term value.
4. Foster a Positive Work Environment: A healthy work culture can boost productivity. Ensure developers have the tools, resources, and support they need to succeed.
5. Regular Feedback and Reviews: Implement regular code reviews, peer feedback, and performance evaluations to help developers improve their skills and productivity.
Modern Tools for Measuring Developer Productivity
Numerous modern tools and platforms can help track and measure developer productivity:
Onetab: An AI powered platform that optimizes communication and collaboration for software developers by streamlining all the developer tools into one platform.
GitHub Insights and GitLab Analytics: These tools provide insights into code commits, pull requests, and collaboration patterns.
Jira Service Management and Trello : Project management tools that track task completion, aiding in measuring output and productivity.
These are just a few examples but I am building a complete guide for software developer, no code automation and productivity and efficiency platforms.
Conclusion
Measuring developer productivity is a complex task that requires a thoughtful approach. While traditional metrics can provide some insights, a more holistic view that emphasizes code quality, teamwork, and real-world impact is often more beneficial. By combining multiple metrics and adding in deep insights through AI and fostering a positive work environment, organizations can effectively measure and improve developer productivity.
